Climate change is a major threat to Indigenous peoples’ rights and health. Indigenous communities are most directly affected by the effects of climate change. Many of these impacts occur at a regional and individual level. Indigenous peoples have unique ways in which to understand climate change. Their knowledge systems are documented in the academic literature. Each generation has had to renew them. Yet, Indigenous communities remain geographically isolated and are often underrepresented in mainstream media. They are thus often denied the opportunity of shaping public debate and policy regarding climate change.
Research into climate change coverage in high-income countries has shown that Indigenous issues and climate change are often underrepresented. Although some articles have discussed the positive effects of climate change, the majority of articles are focused on the negative. Therefore, efforts to combat climate change must take into account the needs of Indigenous Peoples as well as their worldviews. But mainstream media can be a valuable platform for Indigenous peoples in challenging dominant narratives. This study examined 92 newspaper articles in high-income nations over the past 20 years.
A variety of articles were found by searching for climate change. These articles included articles discussing climate change economic impacts, Indigenous communities being responsible for it, as well as articles about how to respond to it economically. These results indicated that the most common description of climate change's adverse effects was "continuous or substantial". On the other hand, the benefits of responding to climate change were more frequently discussed as positive impacts.
Several of the articles focused on the Inuit's experience of climate change. One journalist suggested that Inuit communities were responsible of putting pressure on hunting bans, which in turn led to the endangerment of polar bear populations. Similarly, another article profiled the Inuit's experiences of ice melt in the Arctic. Both articles contained overtly racist and oversimplified frames of Indigenous issues. Also, articles were written about Indigenous communities or Indigenous peoples. The Dene and Navajo were the most prominent. The potential effects of government initiatives on Indigenous communities was the third article.

Other studies have highlighted the important role that media can play in shaping public understanding of climate change. Media coverage can have a substantial impact on Indigenous peoples' accessing funding streams and resources. It can also influence how the general public views Indigenous issues. While the mainstream media has a large role, not many studies have explored the impact of environmental reporting on Indigenous peoples. Some studies have shown that the portrayal of Indigenous peoples in the mainstream media is inaccurate and often focuses on negative impacts instead of positive ones. Mainstream news media frequently perpetuates racism in their portrayal of Indigenous peoples. They fail to recognize the unique and complex nature Indigenous Peoples' contribution to the planet.
It is critical that Indigenous Peoples and Nations continue to work towards developing a climate policy that is Indigenous-led. These policies should be developed in consultation to tribal leadership.
FAQ
How can the impact of climate change be reduced or mitigated?
There are many ways to reduce or mitigate the impact of climate change. There are many ways to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. These include using more sustainable energy and alternative sources of power. Protecting forests and wilderness habitats. Investing in sustainable transport systems. Strengthening early warning systems for natural disasters. Creating a research program about the impacts of climate change on biodiversity. Investing in green technologies like solar panels and wind turbines. Developing sustainable consumption habits and implementing appropriate environmental regulations in all areas of society. It is important to increase public awareness about climate change as it makes people feel accountable for their actions.
What are the environmental and social effects of climate changes?
Climate change has many impacts on society and the environment. Climate change can have many effects on the environment. These changes could have serious consequences for humans, causing instability in communities, intensifying poverty, insect-borne illnesses, changing human migration patterns, and destroying essential habitats.
Already, climate changes are having wide-ranging and profound effects on the environment worldwide. As global temperatures continue to rise, this is likely to worsen in the near future.
The most significant effect of climate change globally is the rise in ocean levels caused by melting ice caps. This leads to shoreline erosion at many coasts as well as an increased risk for flooding for coastal communities. Saltwater intrusion is also a problem, and can negatively impact freshwater supplies along the coasts of many countries.
Due to climate change, extreme weather phenomena such as heatwaves/droughts frequently occur across many countries in the world. These events cause massive destruction to homes, businesses, and sometimes even wipe out entire towns. Additionally, severe storms pose additional risks due to flooding or landlides that can increase damage to infrastructure such roads and railways.
Climate change is also causing wildfires to become more frequent than ever before. This can have devastating effects on habitats as well as people living near them.
This drastic change in living conditions is often a result of displacement or even refugee situations. When people decide to leave their homes, either involuntarily or voluntarily, it can be because their town has become too dangerous or not habitable due the changed climate conditions.
People with respiratory diseases such as asthma are particularly vulnerable to dust storms from increased aridity. Furthermore, pest infestations are predicted to rise in tandem with warmer temperatures. This phenomenon is known as the 'greenhousebug'. Global food insecurity will continue to grow as fewer crops have lower nutritional qualities. This could potentially lead to more hardships for people already struggling to make ends work.
What role does climate change play in greenhouse gas emissions?
Greenhouse gases are a key factor in climate change. They act like an invisible blanket around the Earth, trapping infrared radiation and warming the atmosphere. Without them, our planet would be much cooler than it is now.
Human activity can cause greenhouse gases, such as the burning of fossil fuels and other industries that emit emissions. As more heat enters the atmosphere from these activities, it leads to increased temperatures and extreme weather.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the most common greenhouse gas. It is produced when fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas are burned. Climate change is also caused by major greenhouse gases like methane (CH4) and nitrous oxides (N2O).
Because of human activities, the concentrations of greenhouse gases have increased substantially since preindustrial days. This has led to global warming and an increase in temperatures all over the world, as well as in our oceans. It is also causing major changes such as stronger storms and more droughts, melting of glaciers, rising sea levels, and increased flooding.
To avoid further damage from climate change, humans need to reduce their emissions of greenhouse gases by transitioning away from fossil fuels towards renewable energy sources like solar or wind power. We can also adopt reforestation methods or agricultural methods that allow the soil absorb more CO2 in the air. These activities will help lower atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases and create a healthier environment for all life on Earth.
How does the politics of climate change impact global efforts to address it?
Climate change is a controversial issue that has caused a lot of division between nations, governments and individuals. Politicians of many actors influence the implementation of actions to address climate change. It has been difficult for global consensus to address this urgent environment crisis.
The vast majority of scientific opinion agrees that human-generated climate change is real and requires urgent action. These politics often hamper global cooperation needed to achieve effective progress in implementing sustainable energy practices.
Many governments around the globe want to protect business interests and enforce policies that restrict business activities. This often clashes with regulations that experts recommend for effectively addressing climate change. Without strong commitments from all participating countries and wide-scale international action, it becomes very difficult for any single state or group of states to adequately address climate change through legislation or otherwise.
Differences in power dynamics among countries further complicate gaining full consensus on how best to tackle climate change. Countries with greater economic power are more likely to elect their own representatives to the international bodies responsible for negotiations on the environment. This can cause lopsided discussions about the interests of each country versus the collective interest all parties. The potential side effects of radical change like geoengineering, have been extensively discussed at both the national level and internationally.
At a grassroots level too, grassroots movements have struggled against powerful opponents including corporate ownerships and well-funded lobbies trying to maintain politically favorable positions for their industries especially when it comes to funding research into alternative forms of energy production or enforcing renewable energy technology mandates such as low emissions targets for vehicles etcetera - meaning individual governments must remain clearheaded about potential rewards and outcomes if they are going actively try to make valid progress on the matter in the question itself instead seeking public favor through short-term gains or even spectacles.
It is essential to distribute resources properly to any intervention program, and to be mindful of political divisions within nations, if we want to see an effective coordinated effort to mitigate our current environmental crisis.
How do climate change and global warming impact agriculture and food security?
Climate change, global warming, and other factors have direct impacts on agriculture and food supply. The changing climate can affect rainfall patterns, temperatures, soil moisture levels, and extreme weather. This can cause disruptions in farming, decrease crop yields, and result in a loss of agricultural biodiversity. Warmer temperatures can increase the spread of diseases or pests that can impact crops and can also lead to shifts in the areas suitable for agriculture production. This can increase food production costs, as well as cause hunger and other nutritional problems worldwide.
Rising sea levels present a new threat. They can inundate agricultural land in many coastal locations, leading to increased salinity in wetlands where important crops grow. The changing climate has a similar effect on livestock production. High summer temperatures can decrease the fertility rates of animals like goats, sheep, cattle, and sheep. This can in turn lead to lower milk yields, which can increase food security across communities.
The relationship between climate change and global warming is a complex one; however, efforts are being made to mitigate these results through adaptation strategies implemented by governments worldwide such as strategic investments in climate-smart agriculture (CSA). This involves promoting sustainable methods such as crop rotation techniques or genetic diversity through the conservation of native seed varieties, which help protect against negative impacts from extreme weather conditions or other environmental stressors caused by the changing climate. In addition, CSA strategies call for reductions in greenhouse gas emissions through the use of renewable energy sources and the reduction of deforestation-related logging activities.
Farmers around the globe must adopt technology that is more sensitive to climate changes to ensure food security in a changing environment. Improvements must be made within existing infrastructure set-ups so that necessary actions may be taken when critical crop thresholds are hit - this includes introducing stable irrigation networks with adequate access water supplies at times of the year when there is reduced availability due to warmer climates or intense downpours washing away much-needed access water resources outside planting seasons. To truly create lasting solutions that ensure continued adherence to international dietary guidelines regarding quality nutrition within our increasingly variable climates all over the globe - cohesive collaboration between stakeholders ranging from various government administrations at an international level right down to NGOs at local community sites is required.
What is the role of the energy sector in climate change and how can it be addressed?
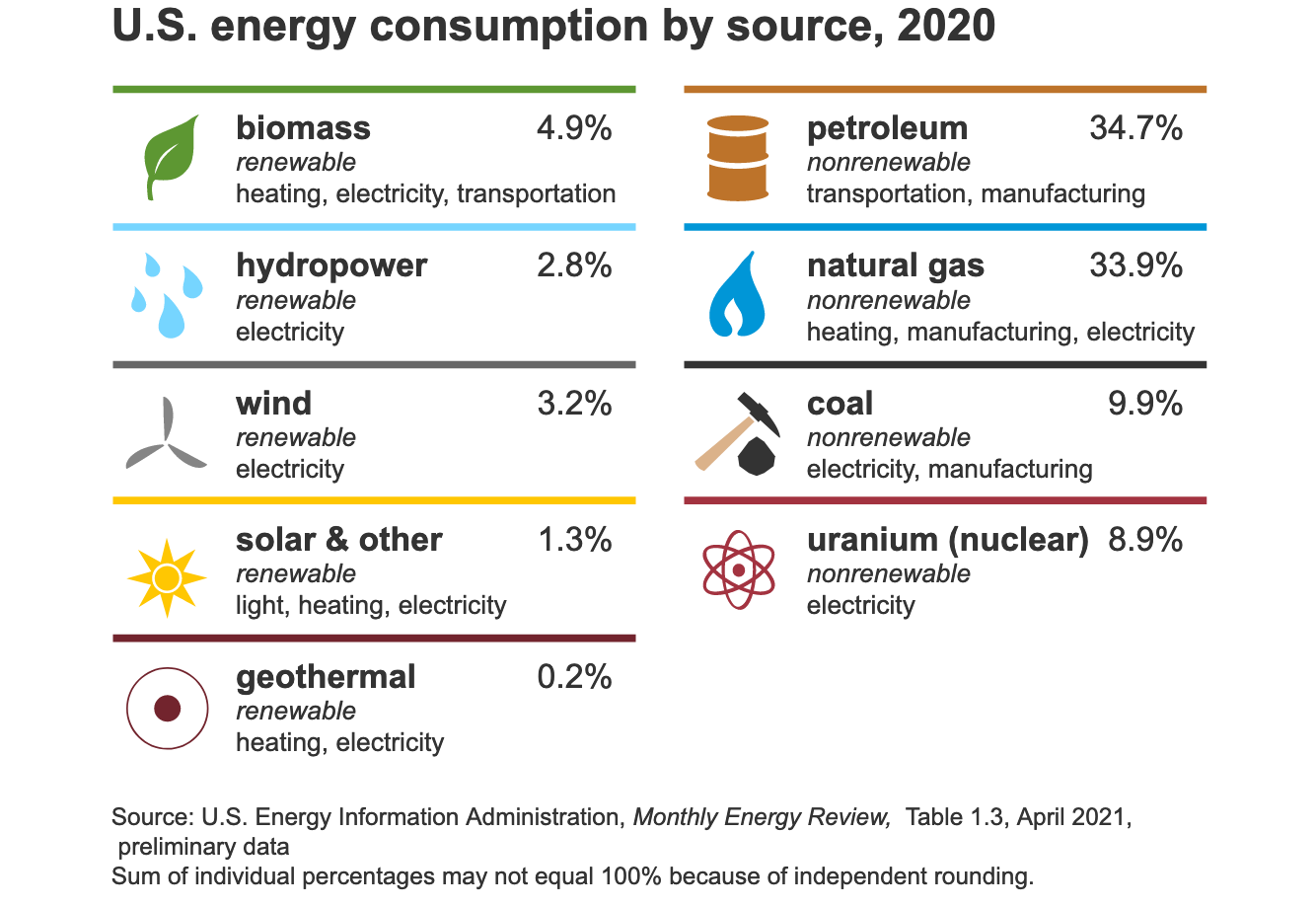
The role of the energy sector in climate change is immense. Global warming can be caused by the burning fossil fuels. The atmosphere releases carbon dioxide, trapping heat and leads to an increase in Earth's temperature.
Energy sources must shift away from fossil-emitting energy sources like coal and natural gases and towards renewable energy sources like wind, solar and geothermal to address this problem. This can be achieved through incentives and government policies, but also by investing in new technology like hydrogen fuel cells. Businesses and households can reduce their carbon emissions by investing in infrastructure to support the use of renewable energy sources.
Another option is to move away from polluting transport options such as petroleum-fueled vehicles and towards electric cars or public transport. Governments can help lead society's transition from oil-based infrastructures to cleaner alternatives by funding research into battery technologies and encouraging consumers to make investments in cleaner modes.
To reduce carbon footprints, companies should adopt green business practices. For example, better insulation in offices and production facilities. This will help reduce operational costs and improve environmental performance.
To be effective, these initiatives need to be supported at both the company and government levels. For example, increasing taxes on polluting products encourages people to change their ways without making them more financially competitive with polluters. Providing vouchers or subsidies to low-carbon products will help create a market that supports sustainability efforts. To sum up, combating climate change will require a huge effort by both the private sector and the public. Switching to renewable energy sources and adopting sustainable practices are key elements to ensuring that future generations are impacted positively.
Statistics
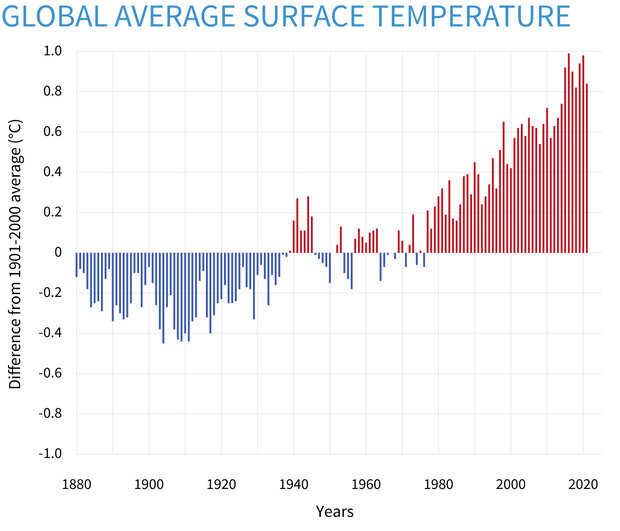
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Support Climate-Friendly Policies and Companies
Individuals can take several steps to support climate-friendly policies and companies. This can include speaking out against non-climate-friendly businesses or politicians, voting for pro-environment candidates, writing letters or emails of encouragement to those who are already taking positive action towards the environment, and signing petitions in favor of policies that encourage and support climate-friendliness. Individuals can also immediately take more practical steps such as switching providers when possible to ones that have a better environmental record or choosing sustainable products over those with higher carbon emissions.
Reducing one's own carbon footprint is an important step in supporting climate-friendly policies and companies. It is possible to make simple changes such as turning off lights and unplugging devices, moving by public transport or carpooling, using eco-friendly household goods like biodegradable cleaning products and composting kitchen wastes instead of adding them to the landfills.
Investors who are keen to support climate-friendly policies will want to find companies that produce lower carbon emissions before investing. Investors interested in climate-friendly policies should examine their portfolios every so often to make sure they are meeting sustainability standards. Investors may want to ensure that their investments in Green bonds do not finance projects with any activity which contributes more greenhouse gases into the air than they take away. Investors should be alert to opportunities where funds can be converted towards green business activities like renewable energy alternatives or other initiatives promoting sustainability, such as community-building projects based on green technologies.