
Climate change has a significant impact on human and animal health. It is crucial for citizens to be aware and prepared for the potential health dangers that climate change may present.
Many health issues can be affected by climate change, including respiratory diseases, foodborne illnesses, and vector-borne disease. Climate change could increase the risk of large-scale fires in certain regions, like the West. People are also more susceptible to respiratory ailments such as asthma and allergic reactions.
Heatwaves are one of the most dangerous climate-related threats to human life. Studies have shown that heat waves with higher frequency are associated with more heat-related deaths as well as complications from cardiovascular and respiratory conditions. Even more people live in areas that are exposed to heat.
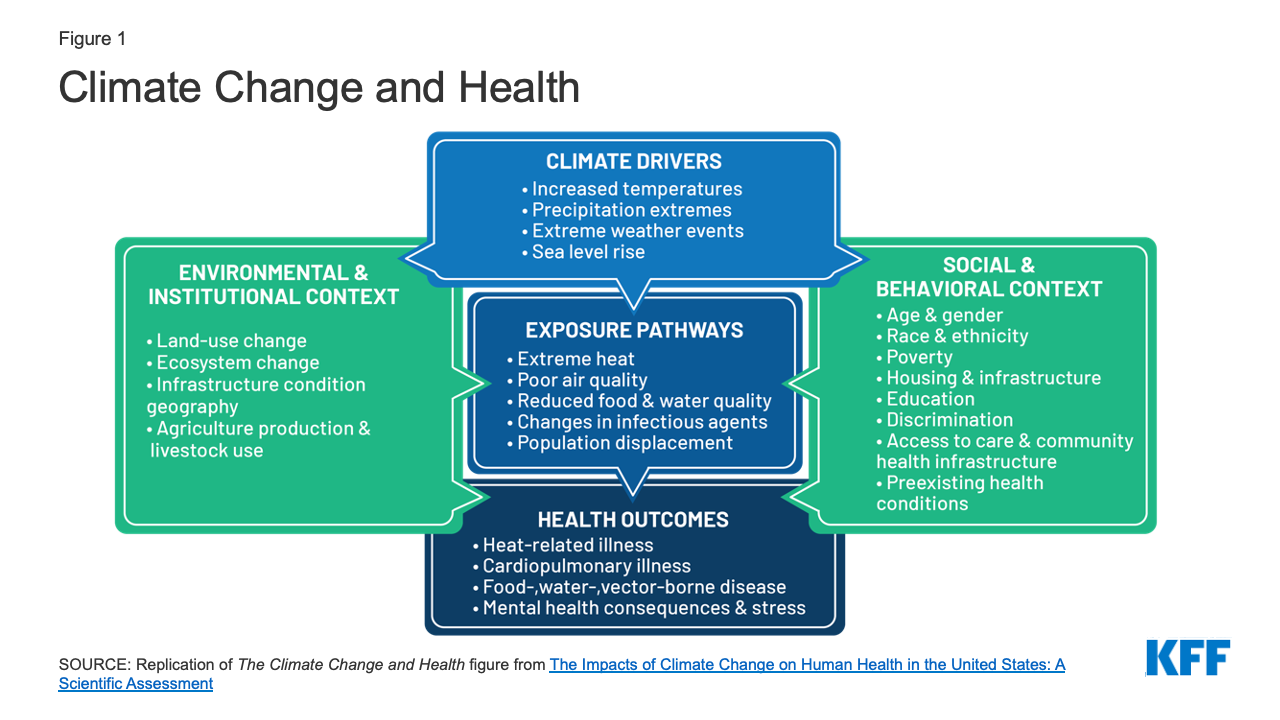
Along with heat-related ailments, people are also at risk for flooding, storms or other extreme events. These events can lead to water contamination by bacteria and other dangerous chemicals. These events may also result in food-borne illnesses such as cholera. Dehydration and severe diarrhea can occur.
Climate change, among other possible effects, is predicted to worsen air pollution. When fossil fuels are burned, it is expected that smog and ground level ozone will rise. These pollutants are expected to increase in levels, causing more severe symptoms such as asthma, cardio-respiratory problems and other respiratory ailments.
Indirect effects of climate changes can have a negative impact on human health. They include the occurrences of infectious diseases like West Nile virus, cholera, and malaria. The incidence of seasonal allergies can increase with changes in pollen levels and ragweed. Storms that are more intense and frequent will cause havoc on land and water.
Vulnerable populations include children, infants, pregnant women and older adults who are particularly vulnerable to climate-related effects. Their location, along with their medical and age, will impact their ability to adapt to the climate change hazards.
Indigenous Peoples of The United States are one of the most at-risk populations. They live in poverty and isolated communities. They rely on the environment to provide their sustenance.
While most Americans are aware that climate change is a threat, many don't think about the impact on their health. People with disabilities and older adults are among the most at-risk.
PAHO's Climate Change and Health Program was created to address the health consequences of climate change. This program will reduce greenhouse gas emissions and encourage climate change adaptation that is health-oriented. PAHO is also planning to provide awards to tribal governments and territories for preparing for and responding to the health impacts of climate change.
Climate change can affect different people in different ways. However, there is no doubt it will have a significant impact on the health and well-being of all Americans. It is estimated that the U.S. will experience thousands of premature mortality by the year 2025, with many more deaths globally. Those in the most vulnerable groups will be at the greatest risk of suffering from climate-related health impacts.
FAQ
How do climate change and global warming impact agriculture and food security?
Global warming and climate change have an immediate impact on agriculture and food safety. Climate change can alter rainfall patterns, temperatures, soil moisture levels and extreme weather. This can impact farming activities, reduce crop yields, or cause loss of agricultural diversity. Warmer temperatures can increase the spread of diseases or pests that can impact crops and can also lead to shifts in the areas suitable for agriculture production. This can increase food production costs, as well as cause hunger and other nutritional problems worldwide.
Rising sea levels pose a further threat. They could inundate valuable agricultural land in many coastal areas, leading to higher salinity levels in wetlands, where important crops are grown. Climate change can also impact livestock production. Warm summer temperatures can reduce the fertility of animals like cows, sheep, and goats. This can cause lower milk yields and increase food insecurity within communities.
Although the relationship between climate change, global warming, and other factors is complex, there are efforts being made by governments to mitigate them through adaptation strategies. These include strategic investments in climate smart agriculture (CSA), which allows governments around the globe to make strategic investments in adapting their agricultural systems. This includes promoting sustainable methods like crop rotation techniques and genetic diversity through conservation of native seed varieties. These help to protect against adverse impacts from extreme weather conditions and other environmental stressors due to the changing climate. In addition, CSA strategies call for reductions in greenhouse gas emissions through the use of renewable energy sources and the reduction of deforestation-related logging activities.
To ensure food security amidst a rapidly changing environment, it will be essential for farmers around the world to adopt technologies that are more sensitive to changes in the climate when it comes to selecting appropriate crops to grow on certain parcels of land. Improvements must be made within existing infrastructure set-ups so that necessary actions may be taken when critical crop thresholds are hit - this includes introducing stable irrigation networks with adequate access water supplies at times of the year when there is reduced availability due to warmer climates or intense downpours washing away much-needed access water resources outside planting seasons. To truly create lasting solutions that ensure continued adherence to international dietary guidelines regarding quality nutrition within our increasingly variable climates all over the globe - cohesive collaboration between stakeholders ranging from various government administrations at an international level right down to NGOs at local community sites is required.
What can be done to reduce or mitigate the effects of climate change?
There are many steps that can be taken in order to reduce and mitigate climate change's effects. These include reducing greenhouse gas emission through more energy efficient practices and using other sources of energy, improving land management practices, protecting forests, wilderness habitats, and protecting against extreme weather events like floods and droughts. It's also important to educate the public about climate change. This will encourage people to be responsible for their actions.
How can human activity impact climate change?
Climate change is a major contributor to human activity. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change(IPCC) states that humans are responsible more than 70% for global warming in the past 20 years.
Burning fossil Fuels: The atmosphere is effected by the combustion of fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas. This increases the already high levels of atmospheric CO2, which acts as a greenhouse gas by trapping heat from Earth's sun and increasing temperatures. This can result in an increase in ocean levels due to Arctic ice melting. This creates unpredictable weather patterns that can disrupt food production and threaten human health.
Deforestation: Trees that sequester atmospheric CO2 in their trunks during photosynthesis are destroyed by deforestation. Also, cutting down forests can increase albedo - which is the amount reflected solar radiation going back into space. It also reduces solar heat absorbtion by the earth's surfaces and encourages excessive global warming. As well decreases local air quality with deforestation being linked permanently with respiratory issues.
Farming: Between 14% and 18% of global anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions are attributed to animal agriculture each year. Animal waste releases large amounts of methane gas into the atmosphere due to its composition rich in methane bacteria Eating less or no animal products altogether can be an effective way to reduce your contribution towards global warming from this source alone., Agriculture itself also relies heavily on fertilizers which contain nitrous oxide released into our atmosphere directly harms humans creating smog from ground level ozone harming our respiratory system making polluted air hazardous for life.
In conclusion, while human activity has had an adverse impact on our environment for centuries, technological advances have made it possible to turn our attention towards the future. We can leverage technology through green innovation to help us move forward in our efforts to reduce climate change and keep everyone safe.
What is the impact of climate change on oceans and marine life around the world?
What will climate change do to the oceans and marine life of the world?
Climate change has been significantly affecting the world's oceans and the associated marine life since its onset. The depletion of the ozone layer, which causes constant oceanic warming, has caused major disruptions to marine ecosystems. This has led to coral bleaching and a decline in species.
Climate change may also be responsible for extreme sea level rises and more unpredictable weather conditions, which can prove to be fatal to coastal areas. Also, rising temperatures can reduce the oxygen levels in the water system, leading to "deadzones" that are areas with less marine life.
Ocean acidification is also a result of excess carbon dioxide that has built up in the oceans. This is due to climate change. Ocean acidification can raise pH levels, making it difficult for animals to adapt like crabs, clams or oysters.
Higher temperatures can also change the location or shrinkage of natural habitats, making them less suitable for some species. An increase in ocean stress can accelerate already high extinction rates of many species around the world, resulting in a severe imbalance between predators/prey that could eventually lead to total extinction.
The effects of climate change ripple throughout entire ecosystems influencing multiple species whether directly or indirectly through evaporation lowering water volumes or sharp temperature shifts jeopardizing any sustainable development for fisheries and other maritime activities. Climate change is transforming the future of all life forms on our planet, not just those living on land but those living below the ocean surface.
Statistics
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Educate Your Communities About Climate Change and Mobilize Action
Climate change education can be in many forms, from online resources and interactive educational tool to classroom activities, simulations, experiential learning programs, and classroom activities. The key elements of effective climate change education are:
-
People with practical knowledge on the subject
-
Showing how individuals can make an impact
-
Participating in an open dialogue regarding potential solutions
-
Inspiration through shared experiences that inspire action
Teachers can assist their communities in reducing their environmental footprint by teaching them comprehensive lessons about climate change.
Connecting scientific research and real-world examples creates a unique opportunity to engage audiences in a meaningful discussion. Participants also have the opportunity to observe positive outcomes and learn from them, which can lead to further innovation or replication within their organizations.
Participants are empowered by incorporating action-oriented activities in educational curriculums. This gives them the mental tools needed to create campaigns, petitions, and take local actions. It also allows them to be agents for social and political change or sustainability improvement initiatives. Moreover, emphasizing individual agency highlights the importance of participation in reducing emissions while also demonstrating participants' collective contributions towards a larger outcome. A key element in policy-making is to involve stakeholders as early as possible. This encourages their active involvement at every stage of the process and could result in better outcomes for all. If we work together to improve public understanding and to take the appropriate action to reduce greenhouse gases emissions, then we might be in a position to create an environment that allows us to address urgent issues with our attention being focused where it is most necessary. In this way, we can all help to achieve our collective goals.