A new report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has detailed described the impact of climate change on planet Earth. It found that if global temperatures are to stay below 1.5 degrees Celsius (C) and to avoid dangerous consequences, nations would need to drastically reduce their anthropogenic carbon dioxide emissions by 2030.
Five major risks are identified by the report. These are heat, droughts, coastal flooding storm surges, and sea level rise. Below is the "burning firecrackers" chart which shows the severity of risks at various levels. Darker colors indicate greater stress levels.

The physical effects of climate change are not the only ones. There are also socioeconomic consequences. Increased risk of flooding and tropical cyclone surges will cause more people to be forced from their homes. This will increase the death toll from extreme weather events. According to the report, the number of people at risk from coastal climate hazards will increase to one billion by 2050.
While many of the impacts of climate change are already occurring, the report notes that the impacts are far larger than previously reported. Many species have been forced to range shifts, with about half of the land animals and plants moving their ranges to areas that are more conducive to survival.
Climate change has not only altered the ecosystems but also made it difficult to access food and water. Millions of people are now experiencing acute food insecurity. Also, the availability of water resources is being diminished by increasing temperature and storminess. Similarly, more than eight million people are currently displaced worldwide by natural disasters.
Over eight percent of terrestrial species are at high risk of extinction. This number is expected rise to 13 percent at three and 15 percent at four degrees. Regional extinctions are also at higher risk.

Increasing sea levels will make flooding more severe, and could lead to major cities exhausting their water resources. Oceans are warming at the same time. This can cause hypoxia. This will reduce the ability of marine microbes to absorb oxygen. In addition, melting Arctic permafrost can release more greenhouse gases to the atmosphere.
A key threat to agricultural production is drought. At two degrees, agricultural droughts are expected to be 150–200% more common. In addition, the expected decline in agricultural yields could be as high as 5 to 10 percent. This could lead to the loss of zinc and other essential nutrients depending on how much CO2 is released.
Changes in the amounts of iron, zinc, protein, and other nutrients are some of the other impacts of climate changes. According to one study, a carbon-equivalent increase of atmospheric CO2 will decrease zinc by 77%. Similar results can be seen for protein. An increase of CO2 equivalent will result in a 4% decrease.
These conclusions are based off climate data from five different global climate models. They are compared against two emission scenarios: one that is low and one that is high. Each of them outlines different methods to achieve macro-level conditions by 2030.
FAQ
How can the world make a transition to a more sustainable future given the challenges presented by climate change?
Sustainability is the ability to meet present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. We must take urgent action to reduce our dependency on finite resources and adopt a more sustainable way of using them.
For a more sustainable future it is essential to rethink our current consumption and production models, as we also need to reduce our dependence upon natural resources such fossil fuels. We must search for new technologies, renewable energies, and systems to reduce harmful emissions, while still meeting our daily requirements.
It is important to adopt an integrated approach to sustainability. This includes considering all aspects, such as the materials used and waste management. It also means incorporating energy utilization in transportation, industry, and industry. There are many possible solutions, such as the use of renewable energy like solar, wind, or hydropower; better waste management; increased efficiency of agriculture; improved transport networks; green construction regulations; and sustainable city planning initiatives.
We need behavioral changes to reach this goal across society. Education programs are essential to assist people in understanding the impacts of climate change. They can also help them understand how they can contribute positively to a more sustainable planet through micro-actions like reducing food waste and adopting low-carbon lifestyles.
Only through cooperation between citizens, business leaders, and governments will we ever be able make substantial progress towards creating a sustainable world for future generations.
What are the ways climate change can be mitigated or reduced?
There are many ways to reduce or mitigate the impact of climate change. There are many ways to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. These include using more sustainable energy and alternative sources of power. Protecting forests and wilderness habitats. Investing in sustainable transport systems. Strengthening early warning systems for natural disasters. Creating a research program about the impacts of climate change on biodiversity. Investing in green technologies like solar panels and wind turbines. Developing sustainable consumption habits and implementing appropriate environmental regulations in all areas of society. It is important to raise awareness of climate change in order to encourage people and make them feel responsible for their actions.
What are the most effective solutions for climate change?
Climate change is a critical issue of our time, and requires the urgent attention of governments, businesses, citizens, and all other stakeholders. Rising temperatures, extreme weather events, increased sea levels, and melting polar ice are clear warnings of a disrupted climate system. Many solutions have been offered to this problem, ranging from technological and behavioral solutions to geoengineering.
Technological Solutions. There are many solutions to climate change that have been developed through technological changes. These include renewable energy sources like solar power and wind power that provide reliable sources for clean energy while causing minimal harm to the environment. Electric cars powered with renewable energy could dramatically reduce pollution in cities and replace petrol vehicles. Other technological solutions include reforestation projects that aim to increase carbon sequestration in trees and soil as well as coastal protection systems to protect vulnerable places against rising ocean levels.
Behavioral changes: Small adjustments to existing routines can make big differences in reducing emissions. This will help limit future climate disruption. Locally produced goods can reduce emissions and transport costs. Public or active transportation can optimize the use of resources, reduce cost and pollution simultaneously. Similarly, more efficient insulation in homes can decrease dependence on gas boilers to heat homes. This will also help lower bills.
Geo-engineering : Geo-engineering refers to large-scale interventions in natural system that have been deemed too risky for potential unforeseen results.
The effectiveness and efficiency of these solutions will depend on how many producers invest in green alternatives. However, incentives such as electric Cars play an integral part in incentivizing alternative solutions. Other than increasing consumer awareness about their utility over time, it is possible to mandate alternative solutions via policies measures. This requires regulatory bodies that are willing to engage players further. Although nontechnological approaches can work at one level; solving the global warming problem requires all parties.
What are the implications of climate change for the environment and society?
Climate Change can have broad impacts on society as well as the environment. Rising global temperatures, extreme weather events, sea level rise, and decreased air quality are just some of the environmental impacts of climate change. These changes can have serious implications for human populations, creating instability in communities, intensifying poverty and insect-borne diseases, altering human migration patterns, and destroying vital habitats.
Already, climate changes are having wide-ranging and profound effects on the environment worldwide. This is expected to get worse as global temperatures continue rising.
Global climate change has one of the most powerful effects on ocean levels. This causes shoreline erosion along many coastlines and increases the risk of flooding for coastal communities. Saltwater intrusion can also happen, affecting freshwater supplies to coastal regions of many countries.
Climate change is causing extreme weather events like heatwaves, droughts and other severe weather to occur in many countries. These events cause mass destruction to homes and businesses, leading to displacement or relocation of communities or wiping out whole towns in some cases. Additionally, severe storms pose additional risks due to flooding or landlides that can increase damage to infrastructure such roads and railways.
Climate change is also causing wildfires to become more frequent than ever before. This can have devastating effects on habitats as well as people living near them.
This drastic change in living conditions is often a result of displacement or even refugee situations. When people decide to leave their homes, either involuntarily or voluntarily, it can be because their town has become too dangerous or not habitable due the changed climate conditions.
People with respiratory diseases such as asthma are particularly vulnerable to dust storms from increased aridity. In addition, pest infestations are expected to increase significantly linked with higher temperature extremes - a phenomenon known as 'greenhouse bug' - leading to further damage to agricultural production that further affects global food insecurity numbers as fewer crops become available at worse nutritional qualities potentially bringing additional hardships upon marginalized populations already barely able make ends meet otherwise.
What impact does climate change have on food security and agriculture?
Climate change and global warming are directly impacting agriculture and food security. Climate change can alter rainfall patterns, temperatures, soil moisture levels and extreme weather. This can affect farming activities and reduce crop yields. It can also lead to a decrease in agricultural biodiversity. Warmer temperatures can increase the spread of diseases or pests that can impact crops and can also lead to shifts in the areas suitable for agriculture production. In turn, this could increase the cost of food production and result in a greater incidence of hunger and poor nutrition worldwide.
Rising sea level poses a risk because they could flood agricultural land along many coasts, causing increased salinity to wetlands. The changing climate has a similar effect on livestock production. High summer temperatures can decrease the fertility rates of animals like goats, sheep, cattle, and sheep. This can in turn lead to lower milk yields, which can increase food security across communities.
Global warming and climate change are complex issues. However, governments around the world are making efforts to reduce these effects through adaptation strategies such as climate-smart agricultural (CSA) strategic investments. This involves encouraging sustainable methods, such a crop rotation technique or the conservation of indigenous seed varieties. This helps to mitigate adverse effects from changing weather or other environmental stressors. In addition, CSA strategies call for reductions in greenhouse gas emissions through the use of renewable energy sources and the reduction of deforestation-related logging activities.
To ensure food security amidst a rapidly changing environment, it will be essential for farmers around the world to adopt technologies that are more sensitive to changes in the climate when it comes to selecting appropriate crops to grow on certain parcels of land. Existing infrastructure must be improved to allow for the appropriate action when necessary. This includes stabilizing irrigation networks that have adequate access to water during periods when there are less water sources due either to extreme downpours or warmer climates. To truly create lasting solutions that ensure continued adherence to international dietary guidelines regarding quality nutrition within our increasingly variable climates all over the globe - cohesive collaboration between stakeholders ranging from various government administrations at an international level right down to NGOs at local community sites is required.
Statistics
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
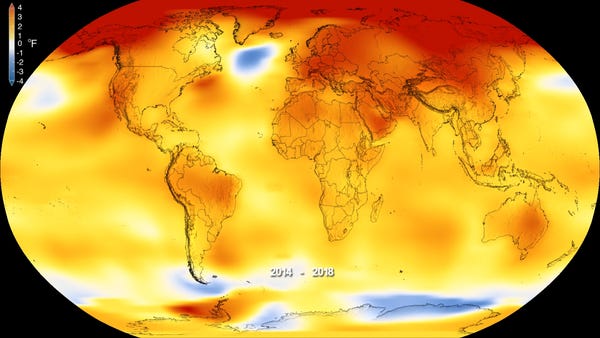
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to integrate sustainable practices into your everyday life to fight climate change
You can implement sustainable practices in your daily life by reducing your consumption. Shopping secondhand and borrowing items from family and friends is a better option than buying new products every day. Eating vegetarian meals at least once a week can reduce methane emissions from livestock production. Also, conserve energy by turning off all lights in a room when you leave it.
Another way to fight climate change is by decreasing emissions from transportation sources like cars and airplanes through carpooling or taking public transit instead of driving alone. Renewable power sources, such as solar panels, can be used to replace traditional fossil fuels. It is crucial to support measures at the policy level that encourage clean air regulations in order to make climate change mitigation work. It is also a great idea to engage with others about issues like plastic pollution and forest destruction. This creates more informed citizens who will take action!